Dillidur 500 Description
Dillidur 500 is a wear-resistant steel plate with a nominal hardness of 500 HBW in the delivery state.
Dillidur 500 is recommended for applications in extremely high-wear environments where materials are required to have excellent machinability, especially excellent welding performance.
Application examples: earth-moving machinery, loading machinery, dredgers, dump trucks, conveying equipment, dump trucks, blades, cut-off crushers, waste treatment and recycling equipment, etc.
Dillidur 500 Wear-Resistant Steel Plate
DILLIDUR 500 is a wear-resistant steel plate with a nominal hardness of 500 HBW in the delivery state.
DILLIDUR 500 is recommended for applications in extremely high-wear environments where materials are required to have excellent machinability, especially excellent welding performance.
Application examples: earth-moving machinery, loading machinery, dredgers, dump trucks, conveying equipment, dump trucks, blades, cut-off crushers, waste treatment and recycling equipment, etc.
DILLIDUR 500 Product Description
Supply size range
According to the supply outline, DILLIDUR 500 is available in thicknesses from 8mm (1/3 inch) 2 to 100mm (4 inches) 2 . Other size requirements can be discussed separately.
DILLIDUR 500 Chemical Composition:
Based on smelting analysis, the following limit values (%) are applicable to each component
| C | Si | Mn | P | S |
| ≤ 0.30 | ≤ 0.70 | ≤ 1.60 | ≤ 0.025 | ≤ 0.010 |
Depending on the thickness, one or more of the following alloying elements will be added:
| Mo | Ni | Cu | Cr | V | Nb | B |
| ≤ 0.50 | ≤ 1.0 | ≤ 0.30 | ≤ 1.50 | ≤ 0.08 | ≤ 0.05 | ≤ 0.005 |
The molten steel is fully sedated and processed for fine graining.
Carbon equivalent reference value:
a CEV =C+Mn/6+(Cr+Mo+V)/5+(Ni+Cu)/15
b CET =C+(Mn+Mo)/10+(Cr+Cu)/20+Ni/40
1 The content of this information is a product description, and may be updated from time to time.
2 The approximate conversion value in parentheses is an offensive reference.
Delivery status:
Temperature controlled water quenching
Mechanical properties in delivery state
Hardness
Brinell hardness of surface at room temperature:
Board thickness ≤ 30mm (1.2 inches) 3 , 470-530 HBW
Board thickness> 30mm (1.2 inches) 3 , 450-530 HBW
Tensile test of transverse specimen at room temperature (reference value for 20mm thick steel plate)
Tensile strength: 1600 MPa (232 ksi) 3
Yield point: 1100 MPa (160 ksi) 3
Elongation: 9% (L o = 5.65 √S o )
Although DILLIDUR has high tensile properties, it is not suitable for applications that emphasize safety. In this case, please use high-strength steel DILLIMAX.
Longitudinal specimen V-notch Charpy impact test (reference value for 20mm thick steel plate)
Charpy impact energy: 25 J at -20°C (-4°F) 3
The Brinell hardness of the test surface is tested every furnace and every 40 tons.
Steel plate mark
If there is no other agreement, the steel plate mark shall include at least the following content:
- Grade (DILLIDUR 500)
- Furnace number
- Motherboard number and steel plate number
- Steel mill sign
- Inspector’s signature
DILLIDUR 500 Processing performance
The whole set of processing technology and application technology adopted by the user is very important to the reliability of the products made from this material. It should be ensured that the design, construction and processing methods are suitable for this material, and meet the requirements of the latest processing technology and the purpose of the product that the processor must follow. The user should select the material by himself, and fully consider the high strength and high hardness of the material, and follow the process recommendations that comply with EN 1011-2 (welding) and CEN/TR 10347 (forming), and comply with national regulations for safe production.
3 The approximate conversion value in parentheses is an offensive reference.
Cold forming
Although DILLIDUR 500 has high hardness and high strength, it can still be cold formed by bending. It should be noted that as the yield strength increases, the forming force required for the steel plate of the same thickness will also increase, and the resilience will also increase. In order to avoid the risk of edge cracking, the flame cut or sheared edge of the cold bending area should be polished. In addition, it is also recommended to smoothly polish the outer edge of the bend that is subjected to tensile stress during bending.
During the processing, necessary safety measures must be taken to ensure that personnel are not exposed to the danger of flying off the workpiece during molding.
Cold forming can usually achieve the following parameters without surface defects (t is the plate thickness):
| Minimum bending radius | Minimum die opening width | |
| Horizontal | 7 t | 16 t |
| Vertical | 9 t | 20 t |
The hardness of hot forming DILLIDUR 500 comes from the accelerated cooling of the austenitizing temperature. If the hardness does not decrease significantly after hot forming, it must be supplemented by subsequent re-quenching treatment. However, the hardness obtained after re-quenching will be different from the hardness tested when the steel plate leaves the factory. This is because the cooling efficiency of the quenching equipment in the processing plant is generally lower than that of the quenching equipment during the production of steel plates.
This material can be heated to about 200°C (390°F) without a significant decrease in hardness.
Flame cutting and welding
Flame cutting should follow the following minimum preheating temperature: plate thickness 26mm and below, 60°C (140°F);
plate thickness 26~70mm and below, 120°C (248°F); plate thickness above 70mm , 150°C (302°F).
Manual arc welding should use alkaline coated electrodes with low residual moisture (if necessary, dry treatment should be carried out according to the requirements of the electrode manufacturer).
In addition, the following suggestions should also be considered:
- For more information on the preheating of DILLIDUR 500, please refer to the technical manual “DILLIDUR-Anti-wear concept”. In any case, preheating above 200 °C (390 °F) must be avoided because it will cause the hardness to decrease (see the figure below).
- It is best to use low yield strength welding consumables for tack welding, root bead and filler bead. If the welding point needs to withstand wear, only use the wear-resistant welding material that can produce the hardness of the mother board in the last weld pass.
Heat treatment
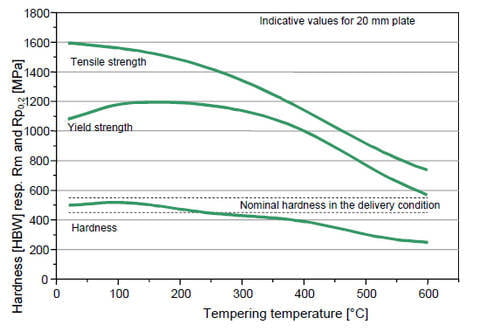 The following figure shows the general change in hardness or strength with heat treatment temperature:
The following figure shows the general change in hardness or strength with heat treatment temperature:
Machining
DILLIDUR 500 can use high-speed steel drills, especially cobalt alloy high-speed drills. If the appropriate drilling speed and drilling speed are used, the drill bit can achieve a satisfactory service life.
General delivery technical requirements
Unless otherwise agreed, the general delivery technology requires the use of EN 10021 standard.
Tolerance
Unless otherwise agreed, the tolerance requirements refer to EN 10029, and the thickness is applicable to A level.
Surface Quality
Unless otherwise agreed, refer to the EN 10163-2 standard and apply A2 level.
Total note
If there are other special requirements for materials that are not covered in this document due to the purpose of use or follow-up process reasons, they can be negotiated before ordering.
The content of this information is a product description and may be updated from time to time.
For more detailed information on the application and processing of DILLIDUR 500, please refer to the technical manual “DILLIDUR-Anti-wear concept”.