1.2311 Steel Description
1.2311 steel, German die steel, the steel is produced by “super pure” process, pre-hardening, showing a high degree of microscopic purity and excellent homogeneous structure, excellent polishing and photoetching.
After heat treatment, processing and polishing performance is good, can be nitriding treatment, suitable for chrome plating and other surface treatment, material hardness uniformity (to 400mm thick), good toughness, good mechanical processing performance. The gold structures are martensite and bainite.
The corresponding national brand number
1.2311 Steel Bar

1.2311 is a pre hardened high tensile tool steel which offers ready machineability in the hardened and tempered condition, therefore does not always require further heat treatment. This eliminates the risks, cost, and waiting time of heat treatment and avoids the associated possibility of distortion or even cracking. Subsequent 1.2311 component modifications can easily be carried out.
Prehardened plastics mould steel with good machinability, better than steel grade Mat. No. 1.2312, suitable for texturing. 1.2311 usually used on Plastic moulds, mould frames for plastic moulds, large injection moulds, pressure casting dies,recipient sleeves.
Applications :
Suitable for large or medium sized and precise plastic moulds. Tools for hot working such as inter-inserts and heat-stressed auxiliary tools. Cavitations Molds, Standard Mould Base, Compression Mould for SMC, blowing mould, Pet preform mold, plastic piping & plumbing injection molds.
Forging:
Heat slowly and uniformly to 1050°C. Do not forge below 930°C. After forging cool slowly.
Annealing:
1.2311 should always be annealed after forging and before rehardening. Heat uniformly to 770/790°C. Soak well and cool slowly in the furnace.
Hardening:
Heat uniformly to 840/870°C until heated through. Quench in oil. Tempering:Heat uniformly the 1.2311 tool thoroughly at the selected tempering temperature and hold at heat for one hour per 25 millimetre of total thickness.
Stress Relieving
Stress relieving to remove machining stresses should be carried out by heating to approx. 650°C, holding for 1-2 hours at heat, followed by air cooling. This operation is performed to reduce distortion during heat treatment.
Physical Properties at ambient temperature Modulus of elasticity [103 x N/mm2]: 210
Density [g/cm3]: 7.83
Thermal conductivity [W/m.K]: 34.0 (100°C), 34.0 (150°C), 33.6 (200°C), 32.9 (250°C), 31.9 (300°C), in quenched and tempered condition.
Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion 10-6 °C-1
Continuous Cooling Transformation (CCT) Diagram
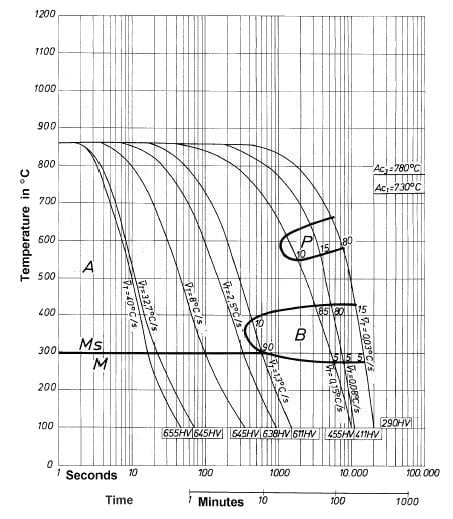
Soft Annealing
Heat to 710-740°C, cool slowly in furnace. This will produce a maximum Brinell hardness of 230.
Tempering Temperature (°C) vs. Hardness (HRC)
Tempering Diagram
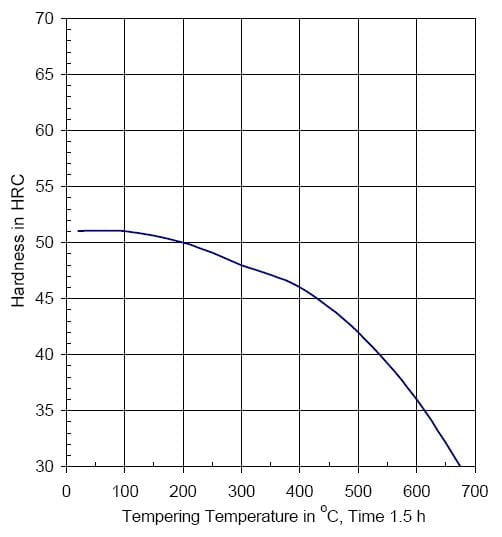
| ||||
C. | Si. | Mn. | Cr. | Mo. |
0.40% | 0.40% | 1.00% | 1.20% | 0.35% |
| Tempering °C | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 |
HRc | 51 | 50 | 48 | 46 | 42 | 36 | 28 |
N/mm² | 1730 | 1670 | 1570 | 1480 | 1330 | 1140 | 920 |
Nitriding:
Moulds machined from pre hardened 1.2311 may be nitrided to give a hard surface which is very resistant to wear and erosion. A nitrided surface also increases the corrosion resistance. The surface hardness after nitriding at a temperature of 525°C in ammonia gas will be approximately 650HV.
Temperature | Time | Approximate Depth of Case |
525°C | 20 hours | 0.30mm |
525°C | 30 hours | 0.35mm |
525°C | 60 hours | 0.50mm |
Tufftriding:
Tufftriding at 570°C will give a surface hardness of approximately 700HV. After 2 hours treatment the hard layer will be approximately 0.01mm
Flame & Induction Hardening:
1.2311 may be flame or induction hardened to a hardenss of 50 to 55 HRc. Cooling in air is a preferable option. Smaller pieces may however require forced cooling. Hardening should be immediately followed by tempering.
Hard Chromium Plating:
After hard chromium plating the steel should be tempered for approximately 4 hours at 180°C, in order to avoid hydrogen embrittlement.
Case Hardening:
In order to maintain maximum surface hardness 1.2311 may be case hardened. Before case hardening is carried out the steel should be annealed. To carburise, pack with carburising powder into a cast iron or heat resisting steel box and see that the articles are separated from the sides by at least two inches of carburising powder. Lute the lid with fireclay. Heat to the carburising temperature of 880°C and soak for sufficient time to give the required depth of case. Cool to 800/820°C and quench in oil. Tempering will then be necessary. Reheat to 200/300°C and allow to cool in the air to give a final surface hardness of Rockwell C55/59
Welding:
Firstly heat to approximately 400 to 500°C. Weld .12311 at approximately 400 to 500°C and stress relieve. Use Chromium-Nickel-Molybdenum alloyed basic electrodes for welding of structural steels. Welding may also be carried out using an austenitic stainless steel electrode. In this case the stipulated increased working temperature may be modified, but the weld metal has a lower strength than the parent material
| Temperature: | ||
| 20°C | 200°C | 400°C | |
| Density (Kg/m³) | 7800 | 7750 | 7700 |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion (per °C from 0°C) | – | 12.7 x 10-6 | 13.6 x 10-6 |
| Thermal conductivity (J/m.s °C) | 29.0 | 29.5 | 31.0 |
| Specific heat (J/kg °C) | 460 | – | – |
| Modulus of elasticity: | |||
| Kp/mm² | 20 900 | 20 400 | 18 900 |
| N/mm² | 205 000 | 200 000 | 185 000 |
| |||
| Turning | Rough | Medium | Finish |
| Carbide Tools | Turning | Turning | Turning |
| Depth of cut (t) mm | min. 10 | 2-10 | max. 2 |
| Feed (s) mm | mm 1.0 | 0.3-1.0 | max. 0.3 |
| ISO Machining Group | P30-P40 | P20-P30 | P10 |
| Cutting Speed | 40-60 | 60-100 | 90-160 |
| ||
| Carbide Tools & | Rough | Finish |
| High Speed Steel Tools | Milling | Milling |
| Depth of cut (t) | min. 2 | max.2 |
| Feed (s) mm/tooth | min. 0.2 | max. 0.2 |
| ISO Machining Group | P30-P40 | P10-P20 |
| Carbide Tools: | ||
| Cutting Speed (v) m/min. | 55-85 | 75-95 |
| High Speed Steel Tools: | ||
| Cutting Speed (v) m/min. | 10-20 | 15-30 |
| |
Tensile Strength | 1000-1068 N/mm² |
Yield Stress | 861-930 N/mm² |
Reduction of Area | 45-50% |
Elongation | 14-17% |













